| CPC G05F 1/10 (2013.01) [G01R 19/2513 (2013.01); H02H 7/20 (2013.01)] | 16 Claims |
|
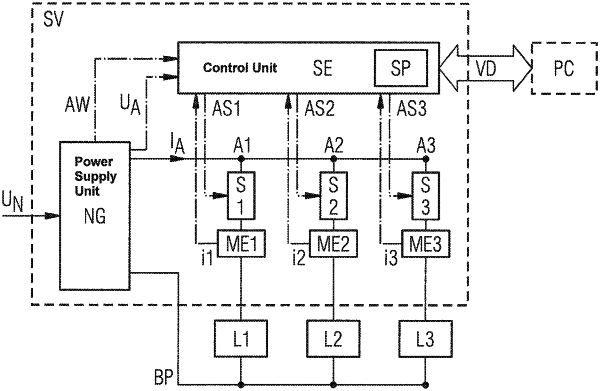
1. A method for monitoring and controlling current distribution in load circuits of an installation control system of a technical installation, a predetermined output voltage being made available by at least one clocked power supply unit and distributed for an energy supply to the load circuits, and at least a plurality of the load circuits being protected by a respective switch unit which are each actuated by a control unit, the method comprising:
measuring, by a respective measuring unit during a learning phase, at least in the load circuits which are protected with the respective switch unit, a current variation of current consumed by each respective load circuit;
deriving and associating at least a significant current profile and an associated tolerance range with each respective load circuit from the current variation measured for each respective load circuit;
continuously monitoring, by the control unit, a current variation which is presently being measured, by the respective measuring unit, at least in the load circuits which are being protected by the respective switch unit during an ongoing operation of the installation;
performing a check to determine whether a power capacity limit is at least reached by the at least one clocked power supply unit; and
reducing and/or switching off current consumed by each load circuit by the control unit by actuating the respective switch unit in those load circuits in which an upper limit of the tolerance range of the significant current profile associated with a respective load circuit is exceeded by a current variation presently being measured for the respective load circuit if the power capacity limit is at least reached by the at least one clocked power supply unit.
|