| CPC G01R 31/086 (2013.01) [G01R 15/18 (2013.01); G01R 23/00 (2013.01); G01R 27/025 (2013.01); G01R 27/08 (2013.01); G01R 27/18 (2013.01); G01R 27/2605 (2013.01)] | 10 Claims |
|
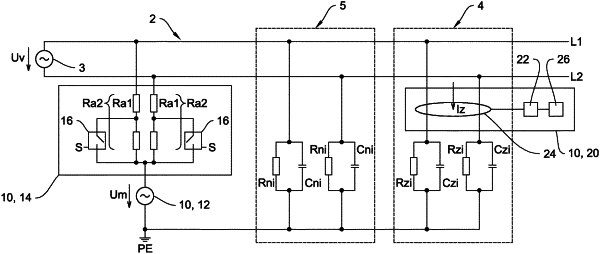
1. A method for determining a branch insulation resistance (Rz) and a branch leakage capacitance (Cz) of a line branch (4) to be monitored in a branched, ungrounded power supply system (2) having active conductors (L1, L2), the method comprising the following steps:
generating a measuring voltage (Um) by means of a controllable measuring voltage source (12);
feeding the measuring voltage (Um) in each active conductor (L1, L2) at a central location of the power supply system (2) by means of a coupling circuit (14);
registering, by means of a current sensor (20), a residual current (Iz) caused by the measuring voltage (Um) in the line branch (4) to be monitored, characterized in that
the measuring voltage (Um) is formed alternatingly a generator period (P) from a first frequency composition (F1) and a second frequency composition (F2), respectively,
the first frequency composition (F1) is fed via a first coupling resistance (Ra1) by means of the coupling circuit (14) switchable using a switching unit (16) and the second frequency composition (F2) is fed via a second coupling resistance (Ra2);
the value of the first coupling resistance (Ra1) and the value of the second coupling resistance (Ra2) and the spectral composition of the first frequency composition (F1) and the spectral composition of the second frequency composition (F2) are stored in a data storage (26) of the current sensor (20);
the current sensor (20) executes a frequency analysis of the residual current (Iz) in a computing unit (22) over two subsequent generator periods (P) in order to identify which frequency composition (F1, F2) is fed presently;
the coupling resistance (Ra1, Ra2) presently switched is determined from the assignment of the identified frequency composition (F1, F2) to the corresponding coupling resistance (Ra1, Ra2) in the computing unit (22);
the branch insulation resistance (Rz) and the branch leakage capacitance (Cz) are computed in the computing unit from the measured residual current (Iz), the measuring voltage (Um), the frequencies contained in the frequency composition (F1, F2), and the coupling resistance (Ra1, Ra2).
|