| CPC F21K 9/90 (2013.01) [F21K 9/64 (2016.08); F21Y 2115/10 (2016.08)] | 26 Claims |
|
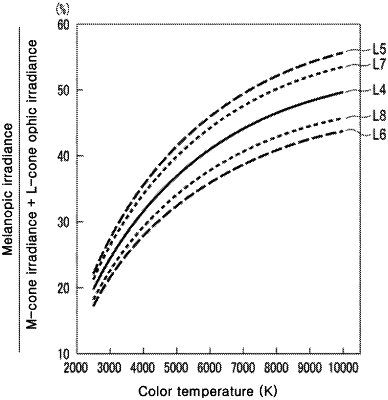
1. A white light source that emits light with a correlated color temperature in a range of 2500K or more to 10000K or less, wherein, when amounts of stimulation light that the white light source irradiates to photoreceptor cells of ipRGC, L cone, and M-cone among human photoreceptor cells are set as melanopic irradiance, L cone optic irradiance, and M-cone optic irradiance, respectively, a ratio of the stimulation light amounts is expressed by the following formula (1), and when the ratio corresponding to an emission spectrum of the above-described white light source is A, and the ratio corresponding to a spectrum of blackbody radiation having a same color temperature as that of the white light source is B, the following formula (2) is satisfied.
Melanopic irradiance/(L cone optic irradiance+M cone optic irradiance) (1)
0.88≤A/B≤1.11 (2)
|