| CPC F01N 11/00 (2013.01) [B01D 53/9418 (2013.01); B01D 53/9431 (2013.01); B01D 53/9495 (2013.01); F01N 3/208 (2013.01); F01N 13/008 (2013.01); B01D 2251/2067 (2013.01); B01D 2257/404 (2013.01); B01D 2258/012 (2013.01); F01N 2550/02 (2013.01); F01N 2900/0601 (2013.01); F01N 2900/1402 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
1. An aftertreatment system for an engine on a work machine, comprising:
a selective catalytic reduction (SCR) system configured for arrangement downstream of the engine and having a dosing system for dosing the SCR system with treatment fluid;
a NOxin sensor arranged at or near an inlet of the SCR system;
a NOxout sensor arranged at or near an outlet of the SCR system; and
an SCR catalyst monitoring module configured to:
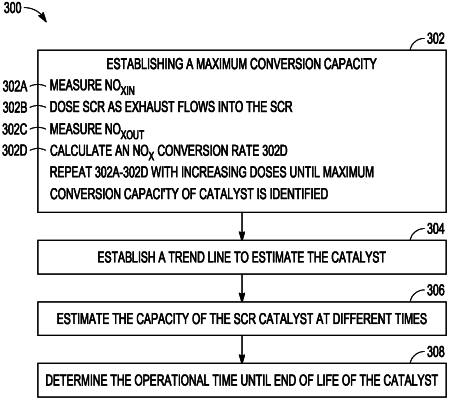
periodically establish a maximum NOx conversion capacity of an SCR catalyst in the SCR system by providing increasing doses of treatment fluid to the SCR system until a threshold is reached; and
establish an SCR deterioration trend based on 2 or more results of the periodically established maximum NOx conversion capacities and a time interval between the results.
|