| CPC C12Q 1/6876 (2013.01) [C12Q 1/6855 (2013.01); C12Q 2600/156 (2013.01)] | 18 Claims |
|
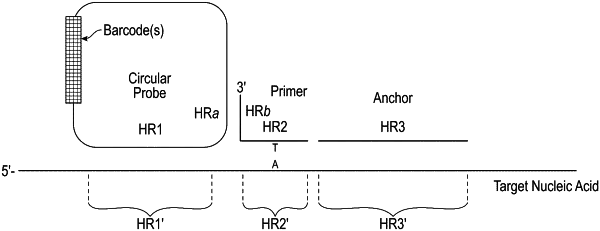
1. A method for analyzing a region of interest in a target nucleic acid, the method comprising:
(i) contacting the target nucleic acid with a circular or padlock probe, a primer, and an anchor to form a hybridization complex, wherein:
the circular or padlock probe comprises adjacent hybridization regions HR1 and HRa, the primer comprises adjacent hybridization regions HRb and HR2, the anchor comprises hybridization region HR3, and the target nucleic acid comprises adjacent hybridization regions HR1′, HR2′, and HR3′, wherein HR2′ or HR3′ comprises the region of interest, and
HR1 hybridizes to HR1′, HRa hybridizes to HRb, HR2 or HR3 comprises at least one nucleotide complementary to the region of interest, and HR2 and HR3 hybridize to HR2′ and HR3′, respectively, thereby hybridizing the circular or padlock probe, the primer, and the anchor to the target nucleic acid;
(ii) ligating the 3′ end of the anchor and the 5′ end of the primer to form a ligated anchor-primer;
(iii) forming an amplification product using the circular probe or a circular probe formed from the padlock probe as a template and the ligated anchor-primer as a primer; and
(iv) detecting the amplification product.
|
|
17. A method for analyzing a single nucleotide of interest in a target mRNA, the method comprising:
(i) contacting the target mRNA with a single-stranded circular probe, a primer, and an anchor to form a hybridization complex, wherein the circular probe, the primer, and the anchor are DNA molecules, and wherein:
the circular probe comprises adjacent hybridization regions HR1 and HRa, the primer comprises adjacent hybridization regions HRb and HR2, the anchor comprises hybridization region HR3, and the target mRNA comprises adjacent hybridization regions HR1′, R2′, and HR3′, wherein HR2′ comprises the single nucleotide of interest,
HR1 hybridizes to HR1′, HRa hybridizes to HRb, HR2 comprises a nucleotide complementary to the single nucleotide of interest and is between 5 and 15 nucleotides in length, and HR2 and HR3 hybridize to R2′ and HR3′, respectively, thereby hybridizing the circular probe, the primer, and the anchor to the target mRNA and directly juxtaposing the 3′ end of the anchor and the 5′ end of the primer;
(ii) ligating the 3′ end of the anchor and the 5′ end of the primer to form a ligated anchor-primer, using a ligase having an RNA-splinted DNA ligase activity and the target mRNA as a template;
(iii) forming a rolling circle amplification product using the circular probe as a template and the ligated anchor-primer as a primer; and
(iv) determining a sequence in the rolling circle amplification product indicative of the single nucleotide of interest.
|
|
18. A method for analyzing a single nucleotide of interest in a target mRNA, the method comprising:
(i) contacting the target mRNA with a primer and an anchor, wherein the primer comprises adjacent hybridization regions HRb and HR2, the anchor comprises hybridization region HR3, and the target mRNA comprises adjacent hybridization regions HR1′, HR2′, and HR3′, wherein R2′ comprises the single nucleotide of interest and HR2 comprises a nucleotide complementary to the single nucleotide of interest and is between 5 and 15 nucleotides in length, and HR2 and HR3 hybridize to R2′ and HR3′, respectively, thereby hybridizing the primer and the anchor to the target mRNA and directly juxtaposing the 3′ end of the anchor and the 5′ end of the primer;
(ii) ligating the 3′ end of the anchor and the 5′ end of the primer to form a ligated anchor-primer hybridized to the target mRNA, using a ligase having an RNA-splinted DNA ligase activity and the target mRNA as a template, at a temperature below the melting temperature (Tm) of the primer for hybridization to the target mRNA, wherein the temperature is above the Tm of the primer for hybridization to the target mRNA when the primer does not comprise the nucleotide complementary to the single nucleotide of interest;
(iii) removing molecules that are not specifically hybridized to the target mRNA;
(iv) contacting the ligated anchor-primer hybridized to the target mRNA with a padlock probe comprising adjacent hybridization regions HR1 and HRa, wherein HR1 hybridizes to HR1′ in the target mRNA and HRa hybridizes to HRb in the primer, wherein the padlock probe is circularized to form a circular probe;
(v) forming a rolling circle amplification product using the circular probe as a template and the ligated anchor-primer as a primer; and
(vi) determining a sequence in the rolling circle amplification product indicative of the single nucleotide of interest.
|