| CPC C08K 3/08 (2013.01) [B29D 11/00125 (2013.01); G02B 1/043 (2013.01); C08K 2003/0806 (2013.01); C08K 2201/003 (2013.01); C08K 2201/011 (2013.01); C08K 2201/013 (2013.01)] | 15 Claims |
|
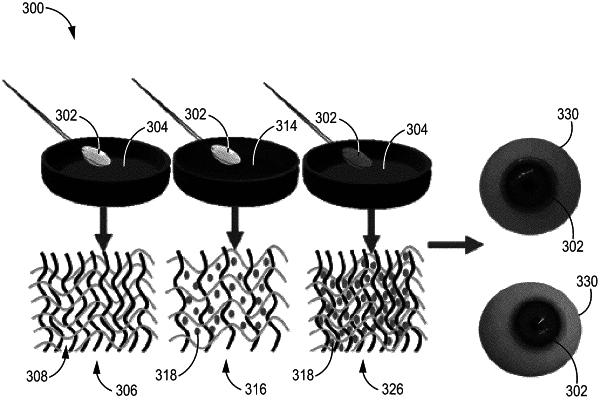
1. A method of incorporating nanoparticles into a contact lens, the method comprising:
contacting a contact lens with a solvent sufficient to remove liquid from the contact lens; and
contacting the contact lens with colloidal nanoparticles sufficient to transfer nanoparticles from the colloidal nanoparticles to the contact lens,
wherein the contact lens includes one or more materials selected from the group consisting of narafilcon A, senofilcon A, etafilcon A, delefilcon A, senofilcon C, comfilcon A, fanfilcon A, ocufilcon D, omafilcon B, somofilcon A, stenfilcon A, hydroxyethyl methacrylate, ethylene glycol dimethylacrylate, polyvinyl pyrrolidone, and a siloxane monomer,
and wherein the diameter of the nanoparticles ranges from 5 nm to 45 nm.
|