| CPC C03C 21/008 (2013.01) [C03C 3/087 (2013.01); C03C 3/091 (2013.01); C03C 17/009 (2013.01); C03C 19/00 (2013.01); G02F 1/133512 (2013.01); C03C 2203/10 (2013.01)] | 9 Claims |
|
1. A glass substrate comprising a pair of main surfaces and an end surface, and
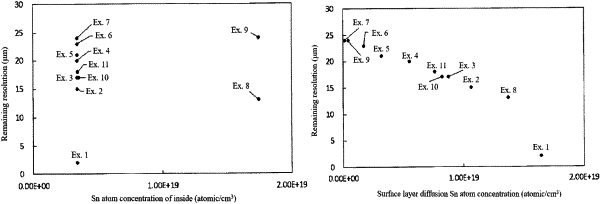
having a surface layer diffusion Sn atom concentration of 2.0×1018 atomic/cm3 or more and 1.4×1019 atomic/cm3 or less in at least one of the main surfaces, the surface layer diffusion Sn atom concentration being obtained by subtracting an Sn atom concentration of an inside of the glass substrate from an Sn atom concentration of a surface layer of the glass substrate,
wherein the Sn atom concentration of a surface layer of the glass substrate is defined as an Sn atom concentration at a depth of 0.1 to 0.3 μm from the main surface and the Sn atom concentration of an inside of the glass substrate is defined as an Sn atom concentration at a depth of 9.0 to 9.2 μm from the main surface,
having an Sn atom concentration gradient of a surface layer of the glass substrate of −1.0×1023 atomic/cm4 or more and −1.0×1022 atomic/cm4 or less in the at least one of the main surfaces,
wherein the Sn atom concentration gradient of a surface layer of the glass substrate is defined as an inclination of a linear function obtained by linearly approximating a depth profile of an Sn atom concentration (atomic/cm3) at a depth of 0.1 to 0.5 μm from the main surface.
|