| CPC B60W 60/0011 (2020.02) [B60W 40/04 (2013.01); B60W 50/0097 (2013.01); B60W 60/0015 (2020.02); B60W 60/00274 (2020.02); B60W 2554/4045 (2020.02); B60W 2554/4046 (2020.02)] | 20 Claims |
|
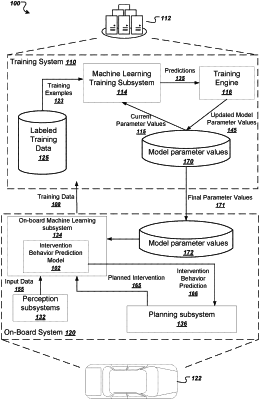
1. A method comprising:
receiving data characterizing a scene that includes a first agent and a second agent in an environment;
processing a confounder prediction input generated from the data using a confounder prediction model, wherein the confounder prediction model is configured to receive the confounder prediction input and to process the confounder prediction input to generate a confounder distribution over a plurality of confounder classes for a confounder variable, wherein the confounder distribution comprises a predicted probability value for each confounder class of the plurality of the confounder classes;
generating a plurality of predicted conditional probability distributions, wherein each predicted conditional probability distribution of the plurality of the predicted conditional probability distributions is conditioned on: (i) a planned intervention by the second agent, and (ii) the confounder variable belonging to a corresponding confounder class, the generating comprises:
for each confounder class, processing an intervention input generated from the data characterizing the scene that includes the first agent and the second agent, the planned intervention by the second agent using a conditional behavior prediction model, and the confounder variable belonging to the corresponding confounder class, wherein the conditional behavior prediction model is configured to receive the intervention input and to process the intervention input to generate a respective predicted conditional probability distribution over a plurality of possible behaviors for the first agent; and
generating an intervention behavior prediction for the first agent based on the plurality of the predicted conditional probability distributions and the confounder distribution, wherein the intervention behavior prediction comprises a probability distribution over the plurality of the possible behaviors for the first agent in reaction to the second agent performing the planned intervention.
|