| CPC A61B 6/12 (2013.01) [A61B 6/032 (2013.01); A61B 6/5247 (2013.01); G06T 7/13 (2017.01); G06T 7/168 (2017.01); G06T 2207/10081 (2013.01); G06T 2207/10116 (2013.01); G06T 2207/10124 (2013.01); G06T 2207/30004 (2013.01); G06T 2207/30204 (2013.01)] | 16 Claims |
|
1. A computer-implemented method for determining an orientation of an electrode for stimulating an anatomical structure, comprising:
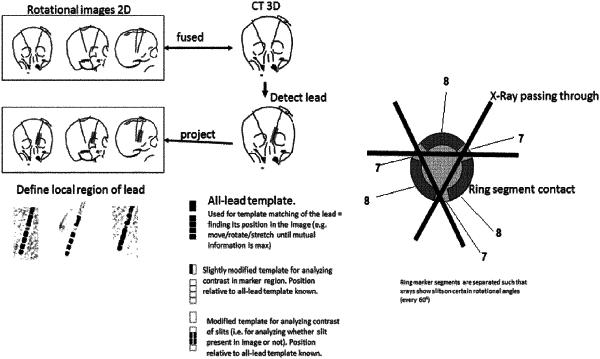
acquiring, by at least one processor, rotational image data describing two-dimensional medical images of the anatomical structure and the electrode, the two-dimensional medical images having been taken with a two-dimensional medical imaging apparatus using an x-ray during rotation of the two-dimensional medical imaging apparatus relative to the anatomical structure, the rotational image data further describing, for each of the two-dimensional medical images, an imaging perspective relative to the anatomical structure associated with the respective two-dimensional medical image and including at least two different imaging perspectives relative to the electrode for stimulating the anatomical structure and implanted in the anatomical structure, the at least two different imaging perspectives having been obtained during rotation of the two-dimensional medical imaging apparatus relative to the anatomical structure, wherein the electrode includes directional contacts extending along at least part of a circumference around a longitude axis of the electrode and divided from one another by slits forming spaces between the directional contacts;
determining, by the at least one processor and based on the rotational image data, rotational orientation data describing a rotational orientation of the electrode in a reference system of the two-dimensional medical images;
verifying, from the two-dimensional medical images generated using the x-ray, the rotational orientation of the electrode described by the rotational orientation data, using the slits between the directional contacts that run parallel to the longitudinal axis of the electrode;
acquiring, by the at least one processor, tomographic image data in a tomographic image data reference system describing a set of tomographic medical images of the anatomical structure; and,
determining, by the at least one processor and based on the rotational image data and the tomographic image data and the rotational orientation data, electrode orientation data describing a rotational orientation of the electrode in the tomographic image data reference system.
|