| CPC A61B 5/7275 (2013.01) [A61B 5/7267 (2013.01); G06N 20/00 (2019.01); G16H 10/20 (2018.01); G16H 10/60 (2018.01); G16H 50/20 (2018.01); G16H 50/70 (2018.01); A61B 5/0022 (2013.01); A61B 5/0205 (2013.01); A61B 5/021 (2013.01); A61B 5/091 (2013.01); A61B 5/14542 (2013.01); A61B 5/14546 (2013.01); A61B 5/4806 (2013.01); A61B 5/4869 (2013.01); A61B 2560/0242 (2013.01)] | 10 Claims |
|
1. A method for predicting susceptibility of a living organism to a medical condition based on one or more machine learning models, comprising:
receiving a request to predict susceptibility of the living organism to the medical condition, the request including a data set of living organism attributes;
generating a feature vector based on the data set of living organism attributes;
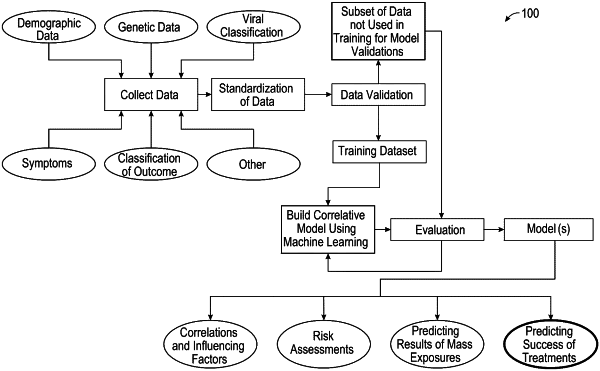
predicting susceptibility of the living organism to the medical condition by generating a prediction using one or more trained machine learning models, the one or more trained machine learning models having been trained based on a featurized data set associating, for each historical living organism of a plurality of historical living organisms, a plurality of data points in medical history for the historical living organism with an indication of whether the historical living organism has the medical condition; and
taking one or more actions to recommend treatments for the living organism based on the predicted susceptibility of the living organism to the medical condition;
wherein the one or more trained machine learning models comprise one or more probabilistic models trained to generate a probability distribution corresponding to a likelihood of the living organism having the medical condition and a likelihood of the living organism not having the medical condition, and
wherein predicting susceptibility of the living organism to the medical condition comprises generating a probability score as a weighted average of probabilities of having the medical condition generated by each of the one or more trained machine learning models, each model of the one or more trained learning model being associated with a weighting value to assign to a likelihood of the living organism having the medical condition.
|