| CPC A61B 5/1464 (2013.01) [A61B 5/0205 (2013.01); A61B 5/14552 (2013.01); A61B 5/7214 (2013.01); A61B 5/725 (2013.01); A61B 5/7257 (2013.01); A61B 5/7278 (2013.01); A61B 5/02411 (2013.01); A61B 5/0816 (2013.01); A61B 5/4356 (2013.01); A61B 2562/0238 (2013.01)] | 24 Claims |
|
1. A method for determining a fetal blood oxygenation level, comprising:
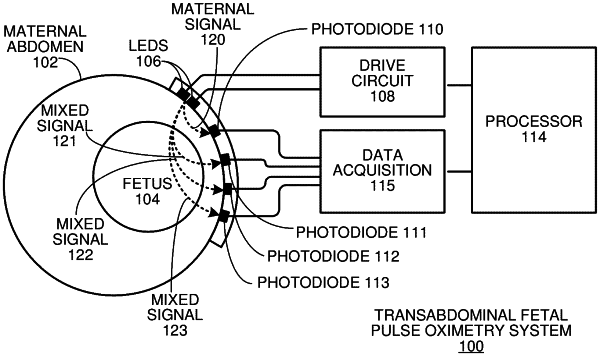
activating two or more light sources, having different wavelengths, which are positioned on the maternal abdomen of a pregnant mammal to direct light into a maternal abdomen toward a fetus;
receiving a set of mixed signals from a set of photodetectors, which are positioned at different locations on the maternal abdomen to receive reflected light from the two or more light sources that traverses both maternal and fetal tissue;
measuring a maternal heart rate through an external maternal heart rate sensor;
measuring a maternal respiration rate through an external maternal respiration rate sensor;
performing a filtering operation that removes signal components associated with the maternal heart rate and the maternal respiration rate from the set of mixed signals to produce a set of fetal signals;
combining the set of fetal signals to produce a composite fetal signal by computing a dynamic weighted average of the set of fetal signals based on dynamic coefficients, which are adjusted based on evolving confidence factors associated with each individual mixed signal; and
determining the fetal blood oxygenation level by performing a pulse-oximetry computation based on the composite fetal signal.
|