| CPC A61B 5/062 (2013.01) [A61M 25/0127 (2013.01); G16H 40/67 (2018.01); A61B 5/287 (2021.01); A61B 2562/0223 (2013.01); A61M 25/09 (2013.01); G16H 20/40 (2018.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
1. A method for obtaining a location or an orientation of an invasive medical device inside a patient, comprising:
receiving, from a plurality of magnetic field sensors arranged in a specific topology separate from the invasive medical device, a first plurality of magnetic field measurements associated with one or more permanent magnets incorporated into the invasive medical device that is at a first position within the patient, wherein the one or more permanent magnets is at a height above the specific topology that is less than or equal to twice a width of the specific topology;
determining the location or the orientation of the invasive medical device at the first position based on the first plurality of magnetic field measurements,
wherein the determining the location or the orientation comprises:
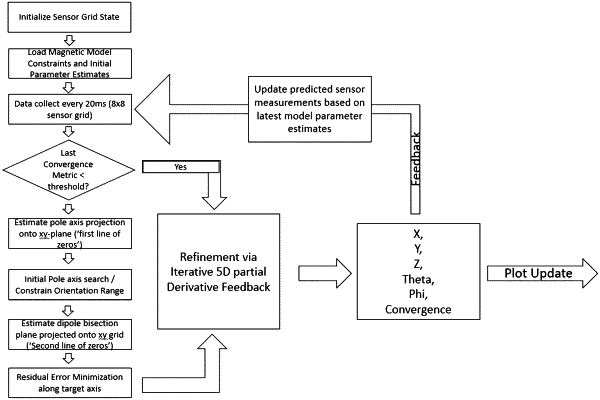
performing, based on the first plurality of magnetic field measurements, a geometric feature extraction calculation to generate an initial estimate for each of a plurality of parameters of a model for the location and the orientation of the invasive medical device, and
performing, based on the first plurality of magnetic field measurements and the initial estimate for each of the plurality of parameters, a refinement calculation to generate a convergence metric and a final estimate for each of the plurality of parameters, wherein the refinement calculation comprises an N-dimensional partial derivative driven convergence method, wherein a predicted value of at least one of the first plurality of magnetic field measurements converges to a corresponding one of the first plurality of magnetic field measurements, and wherein N is a positive integer;
receiving, from the plurality of magnetic field sensors, a second plurality of magnetic field measurements associated with the one or more permanent magnets, wherein the invasive medical device is at a second position within the patient; and
updating the location or the orientation of the invasive medical device by determining the location or the orientation of the invasive medical device at the second position based on the second plurality of magnetic field measurements.
|