| CPC A61B 34/10 (2016.02) [G06F 30/20 (2020.01); A61B 17/846 (2013.01); A61B 2034/102 (2016.02); A61B 2034/105 (2016.02); A61B 2034/107 (2016.02)] | 8 Claims |
|
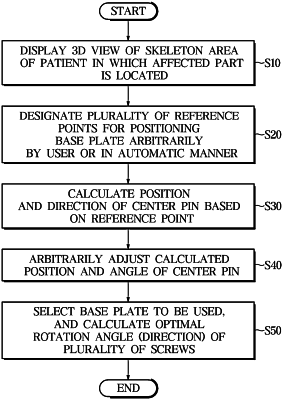
1. A method of designing a guidance specific to a patient, the method comprising:
specifying, by a processor, a first skeletal image plane in which a base plate is to be installed on a skeleton of a patient in which an affected area is located;
displaying, by the processor, a normal vector N of the first skeletal image plane together with the skeleton of the patient in three dimensions (3D);
displaying, by the processor, an intersection of the normal vector and the first skeletal image plane such that an operator arbitrarily moves the intersection or rotates the normal vector based on the intersection to determine a direction of a center pin;
displaying, by the processor, a screen in which the base plate is installed according to a position (a center point) and direction of the center pin determined by the operator; and
calculating, by the processor, a rotation angle and a depth of peripheral screws to be installed on the base plate,
wherein the calculating, by the processor, of the rotation angle and the depth of the peripheral screws to be installed on the base plate includes:
specifying, by the operator, points p of the plurality of peripheral screws to be installed on the base plate; and
rotating, by the processor, the plurality of peripheral screws in an arbitrary range of rotation angles at the specified points of the plurality of peripheral screws, and
wherein the rotating, by the processor, of the plurality of peripheral screws in an arbitrary range of rotation angles at the specified points of the plurality of peripheral screws further includes:
installing, by the processor, the plurality of peripheral screws in a same direction as the center pin at the specified points p of the plurality of peripheral screws;
calculating, by the processor, a distance d from the point of the peripheral screw to an intersection between a ray L in the same direction as the center pin and a triangle formed by arbitrary three points on the skeleton of the patient;
repeatedly calculating, by the processor, the distance d with respect to a preset range of rotation angles (rx, ry) of the ray L; and
based on the rotation angle (rx, ry) at which a maximum distance d is calculated from the repeatedly calculated distances, determining a final rotation angle and a depth corresponding to the maximum distance d, of the peripheral screw.
|