| CPC H04L 61/5046 (2022.05) [H04L 45/20 (2013.01); H04L 45/7453 (2013.01); H04L 47/2483 (2013.01); H04L 61/5007 (2022.05)] | 20 Claims |
|
1. A method comprising:
for a first packet whose destination address is a first Internet Protocol (IP) address, determining by a first network virtualization device (NVD) receiving the first packet that a plurality of IP addresses is associated with the first IP address, wherein the first IP address of the first packet is attached to each compute instance of a plurality of compute instances, each IP address of the plurality of IP addresses is different than the first IP address, and the plurality of IP addresses includes IP addresses of a plurality of NVDs associated with the plurality of compute instances;
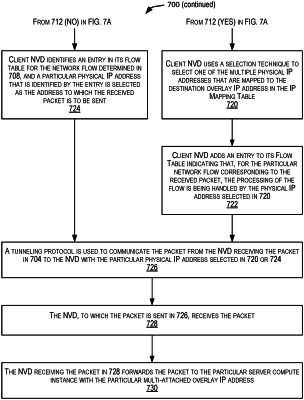
selecting, by the first NVD, a particular IP address from the plurality of IP addresses,
wherein the particular IP address is of a particular NVD from the plurality of NVDs,
wherein the particular NVD is associated with a first compute instance from the plurality of compute instances, and
wherein the particular IP address is selected based on an IP mapping table associated with the particular NVD, wherein the IP mapping table maps the first IP address that is a destination address to one or more of a plurality of physical IP addresses; and
communicating, by the first NVD and using a tunneling protocol, the first packet to the particular IP address that was selected from the plurality of IP addresses, without changing the destination address of the first packet.
|