| CPC H04L 5/1438 (2013.01) [H04L 5/143 (2013.01)] | 30 Claims |
|
1. A wireless communication device for wireless communication, comprising:
a memory; and
one or more processors coupled to the memory, the one or more processors configured to cause the wireless communication device to:
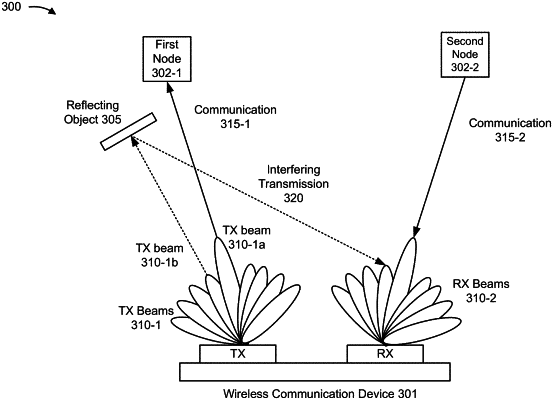
determine, for full-duplex mode communication with a first node and a second node, a first multiple access (MA) signature for the first node and a second MA signature for the second node, wherein the first MA signature and the second MA signature are selected to suppress residual clutter interference; and
communicate in a full-duplex mode with the first node using the first MA signature and with the second node using the second MA signature,
wherein the one or more processors are further configured to cause the wireless communication device to:
determine a timing adjustment to at least one of a first timing or a second timing, wherein the timing adjustment is to cause a delay between reception of a clutter reflection of a first signal and reception of a second signal to be within an adjusted cyclic prefix length of the second signal, wherein the adjusted cyclic prefix length is based at least in part on a scaling factor;
cause the timing adjustment to be applied to the at least one of the first timing or the second timing; and
communicate in the full-duplex mode with the first node and the second node in accordance with the timing adjustment based at least in part on causing the timing adjustment to be applied, wherein communicating includes transmitting the first signal to the first node and receiving the second signal from the second node.
|