| CPC G06Q 30/0185 (2013.01) [G06N 5/046 (2013.01); G06N 20/00 (2019.01); G06Q 20/102 (2013.01); G06Q 20/20 (2013.01); G06Q 20/24 (2013.01); G06Q 20/3224 (2013.01); G06Q 20/34 (2013.01); G06Q 20/401 (2013.01); G06Q 20/407 (2013.01); G06Q 20/409 (2013.01); G06Q 20/4016 (2013.01); G06Q 30/0225 (2013.01); G06Q 30/0248 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
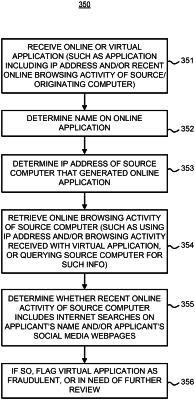
1. A computer-implemented method of identifying fraudulent online applications, the method comprising:
receiving, by a computer system, applicant data associated with an online application;
determining, by the computer system, an IP address of a source computer associated with the online application;
training a machine learning model to determine an online application fraud detection rule, based on historical online application data and corresponding online search activity;
determining, by the computer system, using the online application fraud detection rule, whether online activity associated with the IP address indicates that the online application is potentially fraudulent; and
in response to determining that the online activity indicates that the online application is potentially fraudulent, performing, by the computer system, a fraud mitigation action including at least one of:
flagging the online application as potentially fraudulent; or
generating an electronic alert indicating that the online application is potentially fraudulent.
|