| CPC G01S 19/31 (2013.01) [G01S 19/258 (2013.01); G01S 19/42 (2013.01)] | 22 Claims |
|
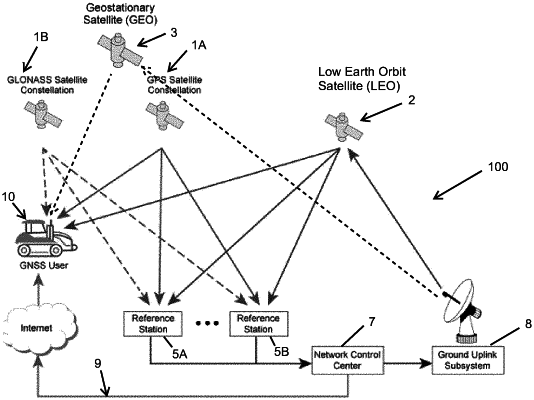
1. A method of enhancing accuracy of a navigation system including a GNSS receiver, the method comprising the steps of:
(a) receiving navigation signals from at least (i) a first GNSS constellation, and (ii) a first LEO constellation;
(b) receiving augmentation data signals from at least one of (i) the first LEO constellation, (ii) a GEO constellation, or (iii) a terrestrial source, wherein the augmentation data includes at least one of (i) wide-area differential GNSS (WADGNSS) data, (ii) Precise Point Positioning (PPP) data, (iii) local-area differential GNSS (LADGNSS) data, or (iv) Real Time Kinematic (RTK) data;
(c) utilizing (1) WADGNSS and/or PPP data to confirm the integrity of (2) the LADGNSS data and/or RTK data, and if the integrity is confirmed, utilizing the LADGNSS data and/or RTK data to correct navigation signals and generate protection levels;
(d) creating at least one position estimate through implementation of a filter using as filter inputs successive readings of at least (i) pseudoranges and carrier-phase measurements from the GNSS constellation, and (ii) carrier-phase measurements from the LEO constellation;
(e) performing Receiver Autonomous Integrity Monitoring (RAIM) by:
(i) using as filter inputs satellite measurements from all satellites within a first set of satellites in order to produce a first filter output,
(ii) iteratively removing as filter inputs satellite measurements from a subset of satellites in the first set in order to produce parallel filter outputs, and
(iii) excluding satellite measurements whose inclusion in the filter inputs creates a parallel output significantly differing from the first filter output.
|