| CPC A61N 1/36139 (2013.01) [A61N 1/3615 (2013.01); A61N 1/36053 (2013.01); A61N 1/36114 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
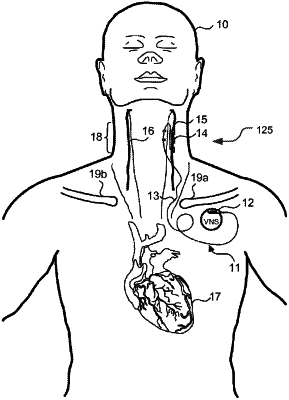
1. A method of operating an implantable medical device (IMD), the method comprising:
generating a plurality of stimulation signals configured to stimulate a nerve of a patient, each stimulation signal of the plurality of stimulation signals having a duty cycle, a frequency, an amplitude, and a pulse width, wherein generating the plurality of stimulation signals comprises adjusting at least one of the duty cycle, the amplitude, or the pulse width while maintaining a fixed frequency across the plurality of stimulation signals;
detecting a cardiac parameter response of the patient during the generation of the plurality of stimulation signals;
identifying a range of the adjusted at least one of the duty cycle, the pulse width, or the amplitude that results in the cardiac parameter response being between a baseline cardiac parameter and a cardiac parameter decrease threshold; and
delivering a plurality of stimulation signals at a duty cycle, a frequency, an amplitude, and a pulse width resulting in the cardiac parameter response being between the baseline cardiac parameter and the cardiac parameter decrease threshold.
|