| CPC H04L 9/0825 (2013.01) [G06F 16/2237 (2019.01); G06F 16/2379 (2019.01); G06F 21/6254 (2013.01); G06N 7/01 (2023.01); H04L 9/008 (2013.01); H04L 9/0643 (2013.01); H04L 9/085 (2013.01); H04L 9/0869 (2013.01); H04L 2209/08 (2013.01); H04L 2209/46 (2013.01)] | 22 Claims |
|
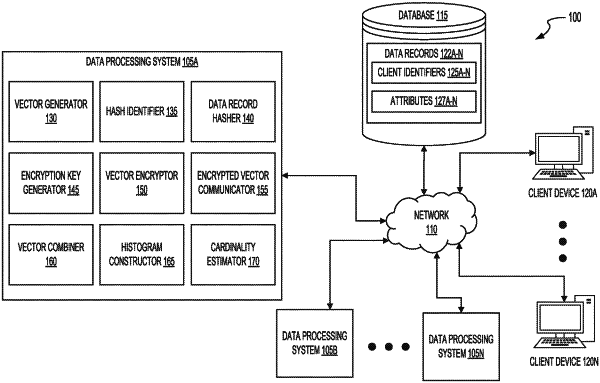
1. A method of efficiently transforming encrypted data structures representing sets of identifiers for secure and computationally efficient network transmission, comprising:
maintaining, by a worker computing device comprising one or more processors and a memory, in the memory, a private decryption key corresponding in part to an aggregated public key;
receiving, by the worker computing device from a publisher computing device, a first encrypted data structure;
decrypting, by the worker computing device, the first encrypted data structure using the private decryption key to generate a partially decrypted data structure;
generating, by the worker computing device, a random variable to determine an amount of noise to add to the partially decrypted data structure;
creating, by the worker computing device, a noise array based on a baseline noise value and a maximum frequency value, the noise array comprising a plurality of noise values;
permuting, by the worker computing device, the noise array to generate a permuted noise array;
encrypting, by the worker computing device, the partially decrypted data structure using a second encryption scheme to generate a second encrypted data structure;
permuting, by the worker computing device, at least two elements of the second encrypted data structure to create a shuffled data structure; and
transmitting, by the worker computing device, the shuffled data structure to a second worker computing device.
|