| CPC H02P 27/08 (2013.01) [H02M 7/5395 (2013.01); H02P 25/026 (2013.01)] | 11 Claims |
|
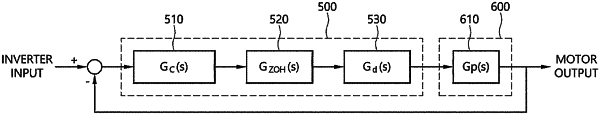
1. An inverter control method in which a controller turns on and off a plurality of switching devices that output an alternating-current (AC) voltage of an inverter using a transfer function of current control, which is a control signal in a discrete time domain, the inverter control method comprising:
generating the transfer function of current control by reflecting a zero-order hold (ZOH) and a time delay and a rotor position and speed of a motor; and
controlling the inverter using the transfer function of current control, wherein generating the transfer function of current control comprises:
generating a first voltage equation for a motor on a stationary coordinate system in a continuous time domain;
reflecting the ZOH and the time delay to the first voltage equation and generating a second voltage equation;
discretizing the second voltage equation and generating a third voltage equation;
reflecting a rotor position and a speed of the motor and generating a fourth voltage equation on a synchronous coordinate system in the discrete time domain;
generating a transfer function of a current control closed-loop on the synchronous coordinate system in the discrete time domain from a transfer function of a current control response characteristic in the discrete time domain; and
generating the transfer function of current control using the transfer function of the current control closed-loop and the fourth voltage equation.
|