| CPC H02N 2/0075 (2013.01) [H02N 2/001 (2013.01)] | 11 Claims |
|
1. A piezoelectric motor energy-saving control method based on an iterative learning, comprising:
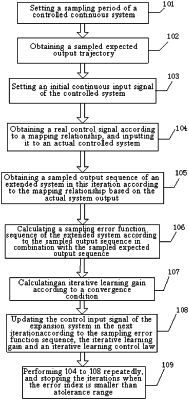
setting a sampling period of a piezoelectric motor;
obtaining an expected output trajectory of the piezoelectric motor, and performing a sampling according to the sampling period to obtain a sampled expected output sequence;
setting an initial control input signal of the piezoelectric motor;
obtaining an actual control input signal according to a mapping relationship of the initial control input signal, and transmitting the actual control input signal to the piezoelectric motor to obtain an actual output position of the piezoelectric motor;
obtaining a mapping relationship of an output position of the piezoelectric motor according to the actual output position, and performing a sampling on the mapping relationship of the output position of the piezoelectric motor according to the sampling period to obtain a sampled actual output sequence;
performing a difference calculation between the sampled expected output sequence and the sampled actual output sequence to obtain a sampling error function sequence;
calculating an iterative learning gain parameter according to a preset convergence condition;
calculating an iterative input voltage required by the piezoelectric motor for performing iterations according to the sampling error function sequence and the iterative learning gain parameter, and transmitting the iterative input voltage to the piezoelectric motor.
|