| CPC G08G 1/0116 (2013.01) [G06V 20/52 (2022.01); G08G 1/0133 (2013.01); G08G 1/0141 (2013.01); G08G 1/0145 (2013.01)] | 10 Claims |
|
1. A computer-implemented method for rapid determining a situation of mixed traffic conflicts, characterized in that, the method comprising the following steps:
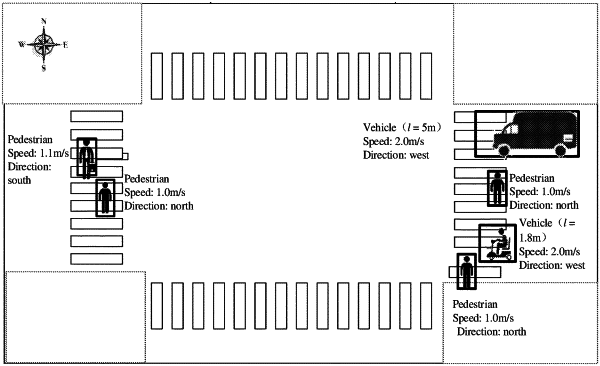
identifying, by a computing device, each of traffic individual units in a road section to be detected by a video camera, the traffic individual units comprises motor vehicles, non-motor vehicles and pedestrians;
obtaining static feature information and dynamic feature information of all traffic individual units within a video detection range, and separating all traffic individual units into two groups of vehicles and pedestrians, by the computing device;
calculating a movement distance of the traffic individual units within a reaction time tr according to a current speed of the traffic individual units, and obtaining critical conflict areas of each of the traffic individual units according to traffic characteristics of the vehicles and the pedestrians, by the computing device;
obtaining intersections of connected conflict areas of each of the traffic individual units, removing intersections of critical conflict areas between the pedestrians, setting intersections of remaining critical conflict areas as potential traffic conflict areas, determining traffic individual units that have intersections in the potential traffic conflict areas as traffic conflict individuals, by the computing device;
calculating an area DC of the critical conflict areas and an unweighted area D of the potential traffic conflict areas of each of the traffic individual units, and then calculating weighted areas of the potential traffic conflict areas, obtaining conflict coefficients ε of the traffic individual units from the area of the critical conflict areas and the weighted areas, by the computing device;
allocating, by the computing device, safety levels of the traffic conflict individuals according to the conflict coefficients.
|