| CPC G06F 9/466 (2013.01) [G06F 9/3009 (2013.01); G06F 9/5033 (2013.01); G06F 9/5083 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
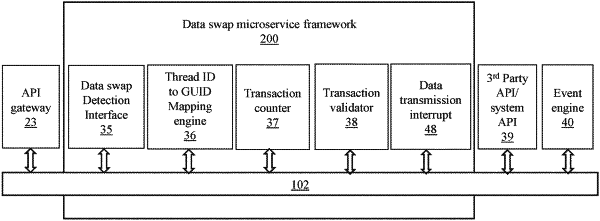
1. A computer-implemented method performed by a data swap microservice framework for preventing incidence of data swaps comprising:
measuring volumeof transactions at transition points that include entry and exit points in distributed computing environment to determine multi-level locations for potential data swaps, wherein each of the transactions has a transaction header;
tagging the transactions with a global user identification (GUID) in the respective transaction header;
recording the entry and exit points from the multi-level locations in the respective transaction header as correlation identifications (CID) for a thread identification (TID);
managing a correlation between the TID and the GUID in the respective transaction header for the transactions in the distributed computing environment by mapping the GUID, the TID, and the CID; and
performing a data transmission interruption to avoid data swaps at the multi-level locations for potential data swaps, based on an exit policy when the CID, the TID, and the GUID for the transactions in the respective transaction header do not match.
|