|
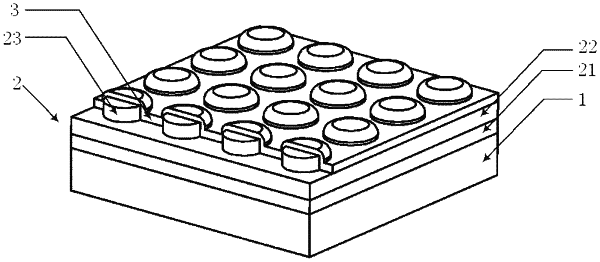
1. An electromagnetic absorption metamaterial having an upper surface in a working environment, the electromagnetic absorption metamaterial comprising: a periodic resonant-unit array, wherein the electromagnetic absorption metamaterial is provided with a layer of dielectric composite film attached to an upper surface of the periodic resonant-array unit array; wherein the dielectric composite film is continuous to provide an even medium environment attached to the upper surface of the periodic resonant-unit array; and said dielectric composite film applies a modulation to surface lattice resonance location and surface lattice resonance intensity of said electromagnetic absorption metamaterial; and the dielectric composite film is obtained by laminating solid dielectric layers of different materials in different thickness proportions, so that the electromagnetic absorption metamaterial can work in any working environment.
|