| CPC G01R 21/00 (2013.01) [G01W 1/10 (2013.01); G01R 22/06 (2013.01); G01R 31/003 (2013.01); G01W 1/18 (2013.01); G06N 20/00 (2019.01)] | 17 Claims |
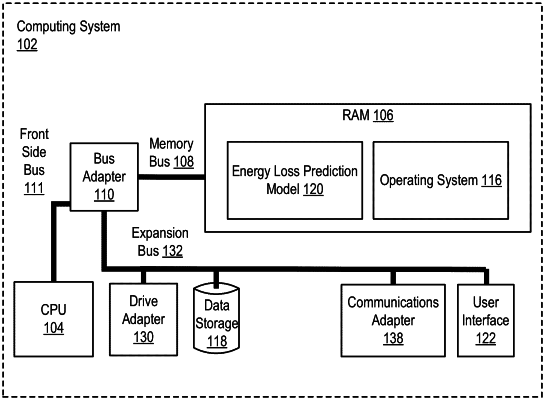
|
1. A method, comprising:
receiving historical meteorological windspeed data associated with a site location of an energy generating device collected during a previous time duration;
receiving historical device windspeed data measured at the energy generating device during the previous time duration;
training, using a machine learning algorithm, a neural network using at least a portion of the historical meteorological windspeed data and the historical device windspeed data;
receiving an alert indicating that windspeed data indicating device windspeeds measured at the energy generating device are unavailable within a particular time duration;
receiving meteorological data associated with the site location of the energy generating device, the meteorological data including meteorological wind speed data collected within the particular time duration; and
predicting one or more estimated device windspeeds at the energy generating device during the particular time duration based on the meteorological data using the neural network for the energy generating device.
|