| CPC G01N 29/2412 (2013.01) [G01N 2291/02854 (2013.01); G01N 2291/0422 (2013.01)] | 5 Claims |
|
1. A method for detecting a defect, in a thickness of an object, occurring due to corrosion and/or erosion, the method comprising:
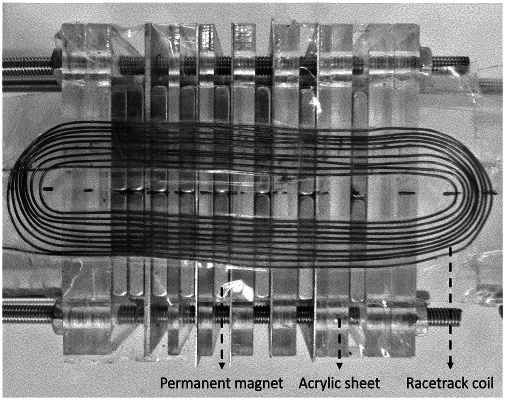
implementing a comb-like pattern transducer, placed along with the object to be tested, for generating a guided wave corresponding to a selected guided wave mode having a cut-off property at a desired range of wavelengths, wherein the desired range of wavelengths is generated by positioning source elements of the comb-like pattern transducer at predefined distances;
providing excitation of the guided wave along the object in a desired range of frequencies, wherein the excitation is performed using broadband excitation techniques comprising at least one of chirp excitation, spike excitation or low cycle Hanning pulse;
receiving at least one of reflected and transmitted guided wave signals in response to the excitation of the guided wave along the object, wherein the at least one of reflected and the transmitted guided wave signals corresponds to defect region of the object;
performing signal processing upon the at least one of reflected and transmitted guided wave signals after being received by:
extracting desired cut-off mode signals by using time domain windows comprising Gaussian window or rectangular window, and
measure at least one of lowest frequency value and highest frequency value of the extracted desired cut-off mode signals by applying time to frequency conversion technique comprising Fast Fourier Transform (FFT), wherein the lowest frequency value is measured upon receiving the reflected guided wave signals and, wherein the highest frequency value is measured upon receiving the transmitted guided wave signals; and
comparing at least one of the lowest frequency value and the highest frequency value to cut-off thickness value of the selected guided wave mode in order to obtain minimum remnant thickness indicating the defect in the thickness of the object,
wherein the selected guided wave mode comprises at least one of a higher order shear horizontal guided wave mode, a higher order anti-symmetric Lamb wave mode, and a higher order symmetric Lamb wave mode.
|