| CPC G01N 21/47 (2013.01) [G01N 15/06 (2013.01); G01N 21/6486 (2013.01); G01N 2015/0038 (2013.01); G01N 2015/0053 (2013.01); G01N 15/075 (2024.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
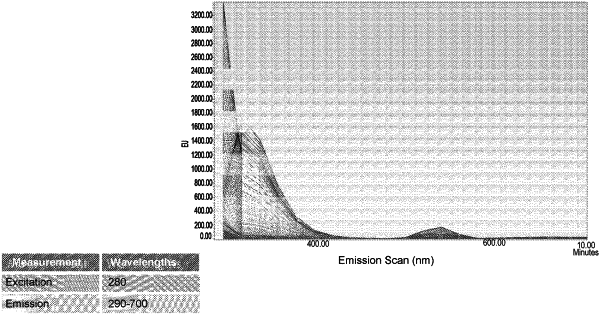
1. A method of detecting a nanoparticle that does not include a dye, fluorophore, marker or an imaging compound, comprising determining a light scattering emission signal from a sample suspected of comprising the nanoparticle,
wherein the light scattering emission signal is not fluorescence or plasmonic and is detected by measuring an emission wavelength from the sample, and when an emission wavelength is detected that is between about 1 nm to about 20 nm longer than an excitation wavelength applied to the sample, the presence of the nanoparticle is indicated,
wherein the nanoparticle does not include a dye, fluorophore, marker or imaging compound,
wherein the nanoparticle is selected from a ribosome, a polymeric bead, a metallic bead, a liposome, a lipid nanoparticle, an exosome, or a combination thereof, and
wherein the light scattering emission signal is determined at an emission wavelength range of about 300 nm to about 600 nm.
|