| CPC G01N 21/3581 (2013.01) [A01G 25/16 (2013.01); G01N 21/3563 (2013.01); G01N 21/84 (2013.01); G01N 33/0098 (2013.01); G06Q 10/04 (2013.01); G06Q 50/02 (2013.01); G01N 2021/8466 (2013.01); G01N 2201/06113 (2013.01); G01N 2201/127 (2013.01)] | 18 Claims |
|
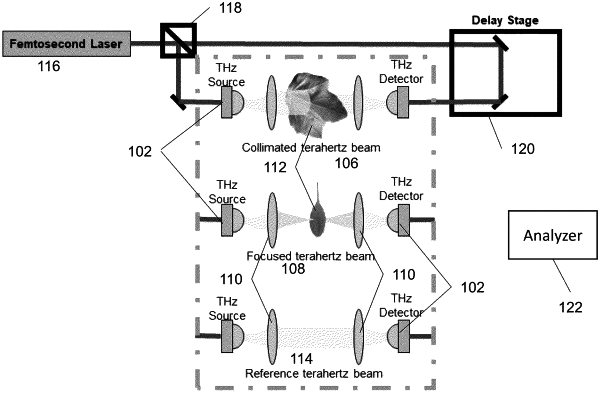
1. A terahertz plant tissue sensing system, comprising:
a terahertz source configured to generate a terahertz beam having a frequency of approximately 100 GHz to approximately 10 THz;
a terahertz detector configured to receive and record a terahertz signal;
at least one optical element to guide the terahertz beam along an optical path from the terahertz source to the terahertz detector, where the optical path impinges on a target plant tissue to generate a signal from the target plant tissue; and
an analyzer to determine at least one water status variable of the target plant tissue based on a field intensity of the signal from the target plant tissue and a field intensity of a reference signal,
wherein the at least one water status variable selected from the group consisting of water mass per area, relative water content, and water potential,
wherein the water mass per area is determined as a function of the field intensity of the signal from the target plant tissue and the field intensity of the reference signal;
wherein the relative water content is determined as a ratio between water mass per area and a saturated water mass per area; and
wherein the water potential (Ψleaf) is determined according to at least one selected from a group consisting of:
a pre-defined calibration curve; and
a sum of a solute potential and a pressure potential.
|