| CPC G01J 5/046 (2013.01) [G01J 5/045 (2013.01); G01J 5/20 (2013.01); H10N 15/15 (2023.02)] | 20 Claims |
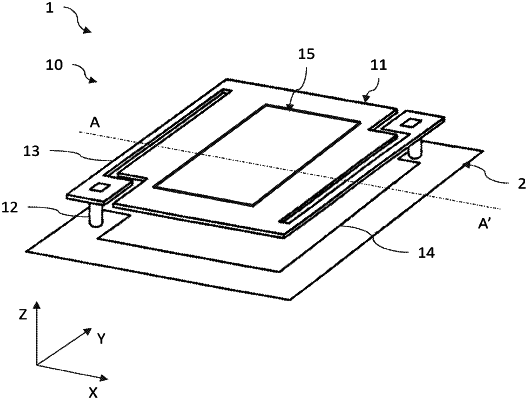
|
1. A process for manufacturing at least one microbolometer, the process comprising:
producing a sensitive material in a thin layer, the sensitive material comprising a first compound comprising vanadium oxide and an additional chemical element, added to the first compound, the additional chemical element comprises arsenic, germanium, silicon, and/or phosphorus, and the additional chemical element comprising no nitrogen;
exposing the sensitive material to a temperature Tr greater than ambient temperature for a duration Δtr, performed after the producing, the temperature Tr and the duration Δtr being such that the first compound, being amorphous and having a native electrical resistivity value at ambient temperature in a range of from 1 to 30 Ω·cm, having undergone exposure to the temperature Tr for the duration Δtr, has an electrical resistivity at ambient temperature less than or equal to 10% of its native value;
determining a non-zero amount of the additional chemical element, referred to as an effective amount, added to the first compound, thus forming a modified compound, starting from which the modified compound, having undergone exposure to the temperature Tr for the duration Δtr, has an electrical resistivity Par at ambient temperature greater than 10% of its native value ρa;
wherein the producing comprises forming the thin layer of the modified compound having an amount of the additional chemical element(s) greater than or equal to the effective amount determined beforehand, the sensitive material being amorphous, having a native electrical resistivity value Pa at ambient temperature in a range of from 0.1 to 30 Ω·cm, and a homogeneous chemical composition;
such that, following the exposing, the sensitive material then has a noise whose degradation has been limited,
wherein the microbolometer comprises the sensitive material,
wherein the process allows noise degradation associated with the sensitive material to be limited.
|