| CPC F24F 11/0001 (2013.01) [F24F 11/74 (2018.01); F24F 2110/12 (2018.01); F24F 2110/30 (2018.01); F24F 2120/10 (2018.01)] | 15 Claims |
|
1. A method for controlling a passive-ventilation system of a building, comprising:
determining an outdoor air temperature (Tout) of air in an environment of the building;
determining an indoor air temperature (Tint) of at least one zone inside the building;
calculating a temperature difference (ΔT) by subtracting the determined outside air temperature (Tout) from the determined indoor air temperature (Tint);
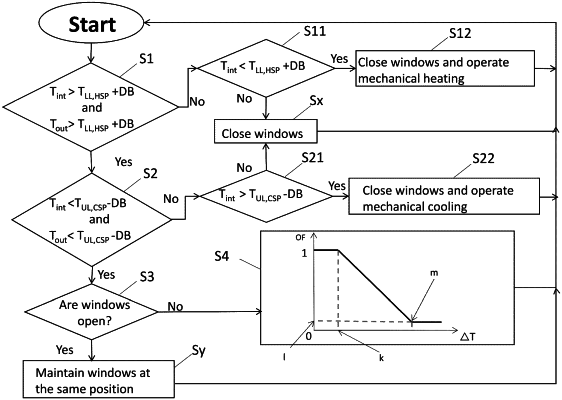
under condition that the calculated temperature difference (ΔT) is greater than zero, controlling a state of at least one passive-ventilation device of the passive-ventilation system to be in any of: a closed state, an open state, or one of one or more intermediate states between the closed state and the open state, where each of the intermediate states corresponds to one value of an opening fraction value (OF) of the at least one zone inside the building varying between 0 and 1, where 0 corresponds to the closed state and 1 corresponds to the open state, and where the at least one passive-ventilation device is configured for a fluidic coupling of at least one respective zone of the at least one zone inside the building with the environment of the building; and
determining, according to a prediction, whether or not the outdoor air temperature (Tout) of the air in the environment of the building will be above an upper outdoor temperature limit in the future within a pre-set lapse of time, and, under condition that the outdoor air temperature (Tout) of the air in the environment of the building will be above the upper outdoor temperature limit in the future within the pre-set lapse of time, the state of the at least one passive-ventilation device is set to a state corresponding to the opening fraction value (OF) higher than that of a state of the at least one passive-ventilation device corresponding to the outdoor temperature determined for a present time or lower than that of the state of the at least one passive-ventilation device corresponding to the outdoor temperature determined for the present time,
wherein the state of the at least one passive-ventilation device is controlled via setting the opening fraction value (OF), the opening fraction value (OF) being set to:
an upper fraction limit equal to 1, under condition where the calculated temperature difference (ΔT) is equal to or below a pre-set lower temperature difference limit (k);
a lower fraction limit (I) equal to or greater than 0 and less than 1, under condition where the calculated temperature difference (ΔT) is equal to or above a pre-set upper temperature difference limit (m); and
a value of a passive-ventilation function of the calculated temperature difference (ΔT) otherwise, the passive-ventilation function monotonically decreasing with increasing calculated temperature difference (ΔT).
|