| CPC F01D 25/166 (2013.01) [F02C 6/12 (2013.01); F02C 7/06 (2013.01); F16C 17/105 (2013.01); F16C 17/107 (2013.01); F05D 2220/40 (2013.01); F05D 2240/53 (2013.01); F16C 2360/24 (2013.01)] | 28 Claims |
|
1. An exhaust gas turbocharger having a hydrodynamic plain bearing, comprising:
a rotor including a rotor bearing surface, the rotor having an axis of rotation;
a counter-bearing part including a counterface, wherein the rotor bearing surface of the rotor and the counterface of the counter-bearing part face each other to form the hydrodynamic plain bearing in the form of a combined journal-thrust bearing having a continuous hydrodynamically load bearing gap formed between the rotor bearing surface and the counterface;
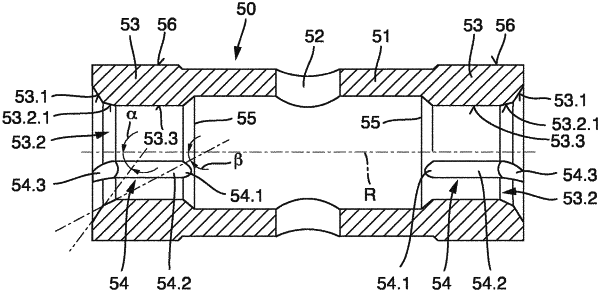
wherein each of the rotor bearing surface and the counterface, when viewed in longitudinal section through the axis of rotation, forms a bearing contour including at least two merging contour sections, the bearing contour being configured to generate hydrodynamic load capacities in both a radial direction and an axial direction; and
wherein a first contour section of the at least two contour sections in sectional view forms a linear section of a cylindrical or partially cylindrical first bearing area;
wherein a further contour section of the at least two contour sections in sectional view in a second bearing area forms a further linear section forming an angle in a range of from greater than 30 degrees to less than 90 degrees with the axis of rotation;
wherein the first contour section and the further contour section merge via a transition section; and
wherein the rotor bearing surface and/or the counterface has at least one lubrication wedge configured to continuously taper the load bearing gap, the at least one lubrication wedge extending at least partially over both the first and second bearing areas and also across the transition section.
|
|
26. An exhaust gas turbocharger having a hydrodynamic plain bearing, comprising:
a rotor including a rotor bearing surface, the rotor having an axis of rotation;
a counter-bearing part including a counterface, wherein the rotor bearing surface of the rotor and the counterface of the counter-bearing part face each other to form the hydrodynamic plain bearing in the form of a combined journal-thrust bearing having a continuous hydrodynamically load bearing gap formed between the rotor bearing surface and the counterface;
wherein each of the rotor bearing surface and the counterface, when viewed in longitudinal section through the axis of rotation, forms a bearing contour including at least two merging contour sections, the bearing contour being configured to generate hydrodynamic load capacities in both a radial direction and an axial direction; and
wherein a first contour section of the at least two contour sections in sectional view forms a linear section of a cylindrical or partially cylindrical first bearing area;
wherein a further contour section of the at least two contour sections in sectional view in a second bearing area forms a further linear section forming an angle in a range of from greater than 30 degrees to less than 90 degrees with the axis of rotation;
wherein the first contour section and the further contour section merge via a transition section; and
wherein the transition section includes at least one linear transition section.
|
|
27. An exhaust gas turbocharger having a hydrodynamic plain bearing, comprising:
a rotor including a rotor bearing surface, the rotor having an axis of rotation;
a counter-bearing part including a counterface, wherein the rotor bearing surface of the rotor and the counterface of the counter-bearing part face each other to form the hydrodynamic plain bearing in the form of a combined journal-thrust bearing having a continuous hydrodynamically load bearing gap formed between the rotor bearing surface and the counterface;
wherein each of the rotor bearing surface and the counterface, when viewed in longitudinal section through the axis of rotation, forms a bearing contour including at least two merging contour sections, the bearing contour being configured to generate hydrodynamic load capacities in both a radial direction and an axial direction; and
wherein a first contour section of the at least two contour sections in sectional view forms a linear section of a cylindrical or partially cylindrical first bearing area;
wherein a further contour section of the at least two contour sections in sectional view in a second bearing area forms a further linear section forming an angle in a range of from greater than 30 degrees to less than 90 degrees with the axis of rotation;
wherein the first contour section and the further contour section merge via a transition section;
wherein the first contour section of the first bearing area and the further contour section of the second bearing area merge indirectly or directly in the transition section via a rounded area; and
wherein the rounded area has a radius in a range of from 0.3 mm to 1.5 mm.
|