| CPC C25B 11/031 (2021.01) [C25B 1/04 (2013.01); C25B 11/061 (2021.01); C25B 11/077 (2021.01); C25B 9/17 (2021.01)] | 17 Claims |
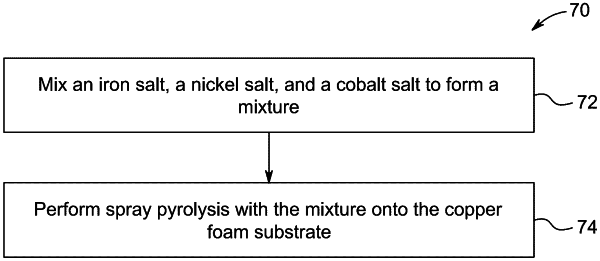
|
1. A method of generating oxygen, comprising:
applying a potential of from 0.1 to 2 V to an electrochemical cell,
wherein the electrochemical cell is at least partially submerged in an aqueous solution,
wherein on the applying the potential the aqueous solution is oxidized forming the oxygen,
wherein the electrochemical cell comprises:
a counter electrode; and
an electrocatalyst,
wherein the electrocatalyst comprises:
a copper foam substrate; and
a nanocomposite comprising:
iron oxide;
cobalt oxide; and
nickel oxide,
wherein particles of the nanocomposite are distributed on a surface of the copper foam substrate,
wherein the particles of the nanocomposite have a spherical shape with an average diameter of less than 500 nm, and
wherein the electrocatalyst comprises 0.1-1 at. % Fe, 0.1-2 at. % Co, 1-5 at. % Ni, 60-70 at. % Cu, and 25-35 at. % O, based on a total number of atoms in the electrocatalyst.
|