| CPC C03C 21/002 (2013.01) [C03C 3/083 (2013.01); C03C 4/18 (2013.01); C03C 2204/00 (2013.01)] | 7 Claims |
|
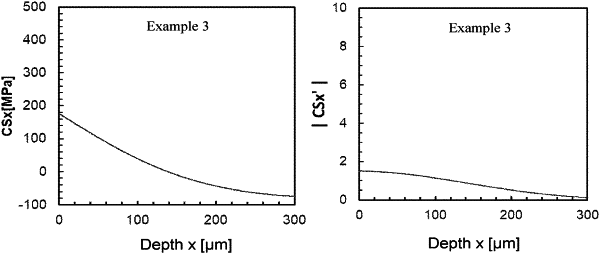
1. A chemically strengthened glass having a thickness t in mm, wherein a first-order derivative CSx′ of a stress value CSx in MPa is −4.7 or larger in a range of CSx≥ 0 in a profile of the stress value CSx in MPa,
wherein the stress value CSx in MPa is a function of a depth x in μm from a glass surface,
wherein the stress value CSx in MPa is measured by a scattered light photoelastic stress meter,
wherein a base composition of the chemically strengthened glass comprises, as represented by mol % based on oxides,
from 52 mol % to 75 mol % of SiO2;
from 8 mol % to 20 mol % of Al2O3;
5 mol % to 16 mol % of Li2O; and
8 mol % or less of Na2O, and
wherein a maximum stress value CS90 at a depth 90 μm from a glass surface satisfies the following inequality:
CS90/{CT2×(t−2×DOL/1,000)}/t≥1.62,
wherein t is the thickness in mm, CT2 is a tensile stress in MPa and DOL is a compressive stress layer depth in μm.
|