| CPC C01B 32/159 (2017.08) [C01B 32/172 (2017.08); C01B 32/174 (2017.08); H10K 85/221 (2023.02); C01B 2202/00 (2013.01); Y10S 977/742 (2013.01); Y10S 977/842 (2013.01); Y10S 977/845 (2013.01)] | 3 Claims |
|
1. A semiconducting carbon nanotube separation method characterized in that the method comprises
a first step of mixing a first substance, a second substance which undergoes two-phase separation when mixed with the first substance in a state of solution, an alkyl chain-containing surfactant, a steroidal surfactant, and a mixture of metallic and semiconducting carbon nanotubes with a solvent, to thereby prepare a dispersion; and
a second step of separating the dispersion into two layers, which are a first layer mainly containing the first substance and a second layer mainly containing the second substance, whereby the semiconducting carbon nanotube is transferred into one of the first layer and the second layer, and the metallic carbon nanotube is transferred into the other of the first layer and the second layer, wherein
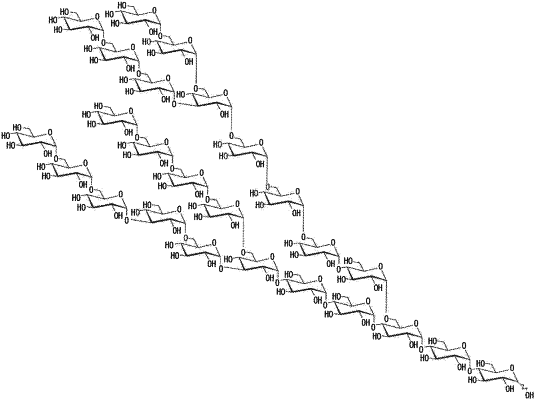
the first substance is an α-glucan which is composed of glucose linked via α-glucosidic linkage and which has a weight average molecular weight Mw of 4,000 to 7,000 and has a ratio in amount of α-1,6 linked glucose residues to the entire glucose residues of 40 to 70%.
|