| CPC A61L 27/48 (2013.01) [A61F 2/30756 (2013.01); A61F 2/3094 (2013.01); A61L 27/52 (2013.01); A61F 2002/30024 (2013.01); A61F 2002/30471 (2013.01); A61F 2002/30761 (2013.01); A61L 2400/12 (2013.01); A61L 2430/06 (2013.01)] | 8 Claims |
|
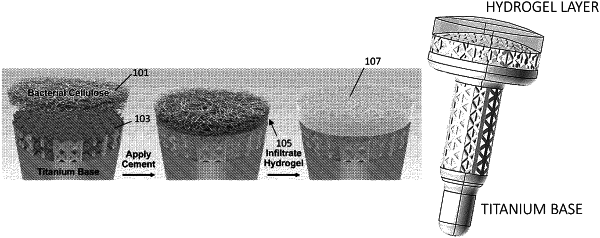
1. An articular cartilage implant, comprising:
an implant body having a top bearing surface;
an anchoring base; and
a cellulose-reinforced hydrogel comprising:
a cross-linked cellulose nanofiber network secured over the top bearing surface of the implant body; and
an interstitial hydrogel portion infiltrated within interstitial regions of the cross-linked cellulose nanofiber network,
wherein the interstitial hydrogel portion is annealed such that a crystalline content of the annealed interstitial hydrogel portion has a crystallinity of 20% or greater,
wherein the cellulose-reinforced hydrogel comprises at least 20% by weight of water,
wherein the cellulose-reinforced hydrogel has a tensile strength exceeding 40 MPa,
wherein the cross-linked cellulose nanofiber network comprises bacterial cellulose (BC).
|