| CPC A61K 31/506 (2013.01) [A61K 45/06 (2013.01); C07C 57/145 (2013.01); C07C 309/04 (2013.01); C07C 309/05 (2013.01); C07D 471/04 (2013.01)] | 18 Claims |
|
1. A method of improving perception, concentration, learning or memory after cognitive impairments occurring in association with a situation, disease, or syndrome selected from the group consisting of mild cognitive impairment, age-associated learning and memory impairments, age-associated memory losses, vascular dementia, craniocerebral trauma, stroke, dementia occurring after stroke, post-traumatic craniocerebral trauma, general concentration impairments, concentration impairments in children with learning and memory problems, Alzheimer's disease, Lewy body dementia, dementia with degeneration of the frontal lobes including Pick's syndrome, Parkinson's disease, progressive nuclear palsy, dementia with corticobasal degeneration, amyolateral sclerosis, Huntington's disease, demyelination, multiple sclerosis, thalamic degeneration, Creutzfeld-Jacob dementia, HIV dementia, schizophrenia with dementia and Korsakoff's psychosis, the method comprising administering a therapeutically effective amount of a compound of formula (I-A)
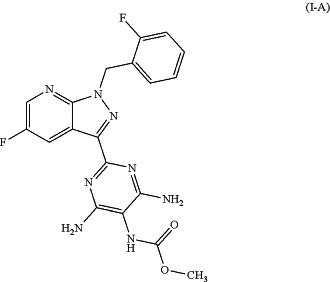 or a salt thereof to a human or animal in need thereof.
|