| CPC A61B 5/18 (2013.01) [A61B 5/372 (2021.01); A61B 5/725 (2013.01); A61B 5/7257 (2013.01); A61B 5/7267 (2013.01)] | 10 Claims |
|
1. A method for controlling a vehicle according to electroencephalography (EEG) signals of a user of the vehicle, comprising, on a processor:
acquiring a plurality of the EEG signals from the user of the vehicle,
determining values for each feature of a predetermined plurality of features of the EEG signals,
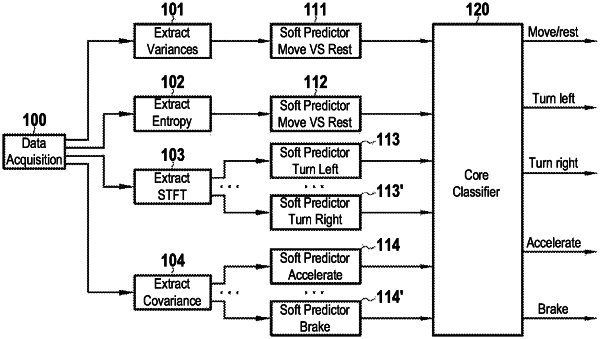
for each feature of the predetermined plurality of features of the EEG signals, performing a respective preliminary soft classification process by at least one trained predictor, of a plurality of trained predictors, corresponding to the feature and taking the values of the feature as input, so as to obtain a plurality of preliminary soft predictions each predicting one of a plurality of predicted driving intentions, each of the plurality of preliminary soft predictions thereby based on a corresponding one of the predetermined plurality of features of the EEG signals,
performing a non-preliminary soft classification process by a trained core classifier taking the plurality of preliminary soft predictions as input, so as to obtain a final driving intention of the user, the trained core classifier being previously trained by machine learning,
wherein the predetermined plurality of features include variances of the EEG signals, differential entropy of the EEG signals, averages of a short-term Fourier transform (STFT) of the EEG signals, and covariances of the EEG signals,
wherein the plurality of predicted driving intentions include an intention to move or rest, an intention to turn left, an intention to turn right, an intention to accelerate, and an intention to brake, and
wherein the plurality of trained predictors include:
a variance-based predictor corresponding to the variances and trained to obtain a preliminary soft prediction of the intention to move or rest, based on the variance values,
an entropy-based predictor corresponding to the differential entropy and trained to obtain a preliminary soft prediction of the intention to move or rest, based on the differential entropy values,
a first STFT predictor corresponding to the averages of the STFT and trained to obtain a preliminary soft prediction of the intention to turn left, based on values of the averages of the STFT,
a second STFT predictor corresponding to the averages of the STFT and trained to obtain a preliminary soft prediction of the intention to turn right, based on the values of the averages of the STFT,
a third STFT predictor corresponding to the averages of the STFT and trained to obtain a preliminary soft prediction of the intention to accelerate, based on the values of the averages of the STFT,
a fourth STFT predictor corresponding to the averages of the STFT and trained to obtain a preliminary soft prediction of the intention to brake, based on the values of the averages of the STFT,
a first covariance predictor corresponding to the covariances and trained to obtain a preliminary soft prediction of the intention to turn left, based on covariance values,
a second covariance predictor corresponding to the covariances and trained to obtain a preliminary soft prediction of the intention to turn right, based on the covariance values,
a third covariance predictor corresponding to the covariances and trained to obtain a preliminary soft prediction of the intention to accelerate, based on the covariance values, and
a fourth covariance predictor corresponding to the covariances and trained to obtain a preliminary soft prediction of the intention to brake, based on the covariance values,
wherein the method further comprises at least one of:
controlling the vehicle to turn left based on the final driving intention of the user indicating to turn left,
controlling the vehicle to turn right based on the final driving intention of the user indicating to turn right,
controlling the vehicle to accelerate based on the final driving intention of the user indicating to accelerate, and
controlling the vehicle to brake based on the final driving intention of the user indicating to brake.
|