| CPC G05B 13/0245 (2013.01) | 28 Claims |
|
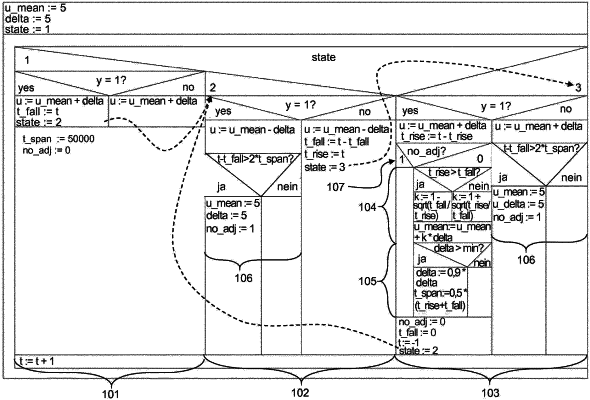
1. A method for two-point control of an actuator acting on a process variable, the method comprising steps of:
generating a binary sensor signal with a sensor that detects the process variable such that the sensor outputs a first sensor signal value when the process variable exceeds a first switching value and the sensor outputs a second sensor signal value when the process value falls below a second switching value;
controlling the actuator by a manipulated variable having only one of a first control value and a second control value, and
dynamically adjusting the first control value and the second control value in dependence on a fall time representing a first duration of the first sensor signal value and a rise time representing a second duration of the second sensor signal value such that during operation of the actuator the rise time and the fall time converge toward each other by repeatedly carrying out
a first sub step in which
the actuator is controlled with the first control value that is set to represent a difference between a mean value of the manipulated variable and an amplitude of the manipulated variable, and
the fall time is determined on the basis of the first sensor signal value;
a second sub step in which
the actuator is controlled with the second control value that is set to represent a sum of the mean value of the manipulated variable and the amplitude of the manipulated variable, and
the rise time is determined sensor on the basis of the second sensor signal value; and
a third sub step in which
a new mean value of the manipulated variable is determined on the basis of the fall time and the rise time.
|