| CPC G01R 31/088 (2013.01) | 7 Claims |
|
1. A method for identifying an arc crosstalk signal based on vector analysis calculation, comprising:
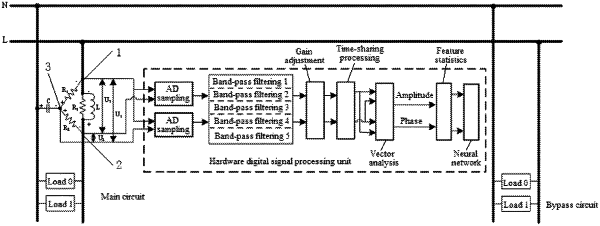
performing sampling, by a sampling circuit, to obtain a voltage signal of an inductor and voltage signal of a first resistor, wherein
the sampling circuit comprises: a first resistor R1, a second resistor R2, a third resistor R3, an inductor L and a capacitor C;
the inductor L is connected in series between a first measurement point and a second measurement point in a live line, the third resistor R3 is connected in parallel with the inductor L, the first resistor R1 is connected in series between the first measuring point and a third measuring point, the second resistor R2 is connected in series between the second measuring point and the third measuring point, the third measuring point is connected to a neutral line via the capacitor C, and a load is connected between the live line and the neutral line; and
in performing sampling, a voltage signal of the inductor between the first measuring point and the second measuring point and a voltage signal of the first resistor between the first measuring point and the third measuring point are collected respectively to analyze whether an arc fault occurs in the sampled line;
calculating a voltage signals of a second resistor based on the voltage signal of the inductor and the voltage signal of the first resistor, determining the voltage signal of the first resistor as a first sampling signal, determining the voltage signal of the second resistor as a second sampling signal, and determining the voltage signal of the inductor as a third sampling signal; and
determining whether a signal in a sampled line is an arc signal or a crosstalk signal based on an amplitude ratio feature vector, an amplitude fluctuation feature vector, an phase difference feature vector and/or a phase fluctuation feature vector, wherein the amplitude ratio feature vector is equal to a ratio of a voltage effective value of the first sampling signal to a voltage effective value of the second sampling signal, the amplitude fluctuation feature vector represents a magnitude relationship between a voltage amplitude fluctuation of the first sampling signal and a voltage amplitude fluctuation of the second sampling signal, the phase difference feature vector is equal to a difference between a phase of the first sampling signal and a phase of the third sampling signal, and the phase fluctuation feature vector is equal to a difference between a phase fluctuation of the first sampling signal and a phase fluctuation of the third sampling signal.
|