| CPC G01N 27/3274 (2013.01) [G01N 27/3273 (2013.01); A61B 5/14532 (2013.01); A61B 2562/0295 (2013.01); G01N 27/3272 (2013.01); G01N 27/3277 (2013.01); G01N 27/4168 (2013.01); G01N 27/48 (2013.01)] | 14 Claims |
|
1. A method for determining a concentration of an analyte in a fluidic sample, the method comprising:
applying the fluidic sample to a biosensor, the biosensor comprising an electrochemical cell having electrodes;
applying a voltage waveform comprising at least a first predetermined voltage applied during a first time interval and a second predetermined voltage different from the first predetermined voltage applied during a second time interval;
measuring at least first current values during the first time interval and second current values during the second time interval;
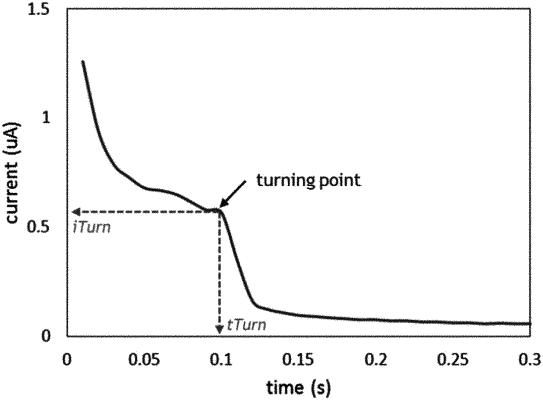
determining a turning point time during the first time interval at which the measured first current values transition from a first profile to a second profile; and
estimating a physical characteristic of the sample based on the turning point time, the first measured current values and the second measured current values;
if the estimated physical characteristic of the sample is in a first range, calculating the concentration of the analyte in the sample using a first model based on the first measured current values and the second measured current values; and
if the estimated physical characteristic of the sample is in a second range, calculating the concentration of the analyte in the sample using a second model based on the determined turning point time, the first measured current values and second measured current values.
|