| CPC F02D 41/18 (2013.01) [F02D 41/0002 (2013.01); F02D 41/1401 (2013.01); F02D 41/185 (2013.01); F02D 41/187 (2013.01); F02D 2009/0255 (2013.01); F02D 2200/0404 (2013.01)] | 8 Claims |
|
1. A control apparatus for an internal combustion engine comprising:
a clogging parameter calculation means that calculates a clogging parameter that represents the degree of clogging of a throttle valve using a first flow rate function for a state where the degree of clogging of the throttle valve in an intake air passage of the internal combustion engine is in the reference state and a second flow rate function estimated based on an intake air volume detected by an air flow meter; and
a control means that controls the internal combustion engine using the calculated clogging parameter,
wherein the clogging parameter calculation means includes:
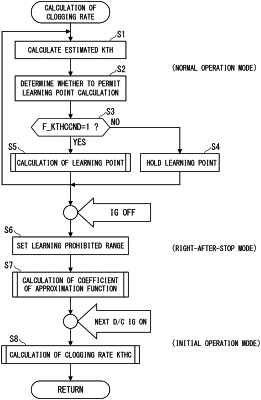
a sample point acquisition means for obtaining sample points that calculates the second flow rate function and obtains sample points, which are combinations of the second flow rate function and the throttle valve position of the throttle valve, for each predetermined period during operation of the internal combustion engine;
a learning point calculation means that calculates learning points for each of a plurality of predetermined position ranges of the throttle valve by averaging the plurality of sample points belonging to the position ranges; and
a coefficient calculation means that calculates coefficients of an approximate function of a predetermined polynomial equation for approximating a second flow rate function characteristic, which represents the relationship of the second flow rate function with the position of the throttle valve, by the least-squares method based on the plurality of learning points calculated for each of the plurality of position ranges, and
the control apparatus calculates the clogging parameter based on the second flow rate function characteristic approximated by the approximate function using the calculated coefficients and on the first flow rate function.
|