| CPC A61N 1/36031 (2017.08) [A61N 1/0484 (2013.01); G06N 20/00 (2019.01); A61N 2007/0021 (2013.01)] | 15 Claims |
|
1. A neuromodulation system comprising:
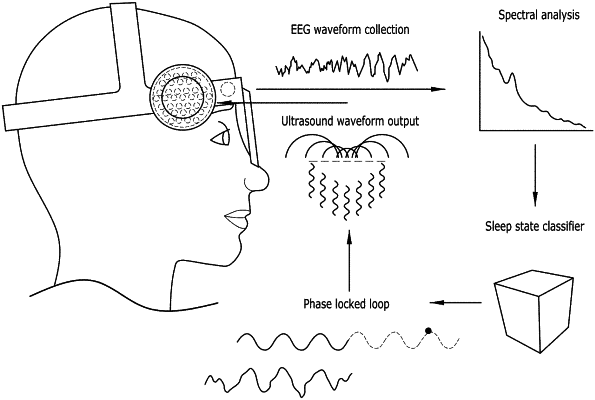
a neuromodulation device including a wearable device housing, one or more EEG electrodes for analyzing brain function in real time, one or more EEG signal amplifiers coupled to the one or more EEG electrodes, and one or more ultrasound-emitting elements; and
a stimulation control computing environment comprising a stimulation control unit and an offline computing device, the stimulation control unit comprising at least one processor coupled to the one or more ultrasound-emitting elements, and configured with one or more data processing functions to focus ultrasound emission to a centromedian thalamus, the one or more data processing functions including:
an offline algorithmic mapping element configured to:
use brain image data to identify the centromedian thalamus, and
perform one or more acoustic simulations to determine information for use in focusing ultrasound emissions from the one or more ultrasound-emitting elements to the centromedian thalamus, and
an online algorithmic stimulation application element configured to:
process real-time data acquired by the one or more EEG electrodes to detect a phase of at least one slow wave, and
control the ultrasound emissions from the one or more ultrasound-emitting elements, in accordance with the waveform parameters determined by the offline algorithmic mapping element, such that the ultrasound emissions constructively interfere at the centromedian thalamus to form a plurality of ultrasound pulses focused on the centromedian thalamus during a certain slow wave phase range for enhancing the at least one slow wave based on the detected phase of the at least one slow wave thereby improving a quality of sleep by the user during a sleep stage, wherein the ultrasound emissions are phase locked to the at least one slow wave such that the ultrasound pulses have a frequency in a range below 2 Hertz.
|