| CPC A61B 34/20 (2016.02) [A61B 5/062 (2013.01); A61B 90/00 (2016.02); A61B 17/00 (2013.01); A61B 2034/2051 (2016.02); A61B 2034/2072 (2016.02); A61B 2090/08021 (2016.02)] | 17 Claims |
|
1. A method for detecting a location and operating state of a surgical instrument having an active operating state, and an inactive state, comprising:
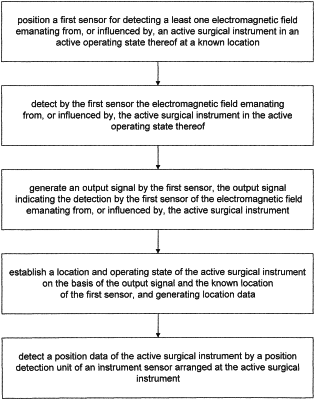
positioning a first sensor at a known location, the first sensor configured to detect a first electromagnetic field emitted from the surgical instrument when in the active operating state;
detecting the first electromagnetic field with the first sensor;
generating an output signal from the first sensor, the output signal indicating the detection by the first sensor of the first electromagnetic field emitted from the surgical instrument in the active operating state; and
establishing the location and the operating state of the surgical instrument in the active operating state on the basis of the output signal and the known location of the first sensor;
generating location data, the location data corresponding to the established location;
controlling the operating state of the surgical instrument based on the output signal;
detecting a second alternating electromagnetic field generated by a field generator with an instrument sensor; and
generating an induced current dependent on a position of the instrument sensor, and evaluating the induced current so as to determine a position of the surgical instrument relative to a patient when the surgical instrument is in the inactive state.
|