| CPC G06F 40/58 (2020.01) [G06V 20/41 (2022.01); G10L 15/19 (2013.01); G10L 15/22 (2013.01)] | 10 Claims |
|
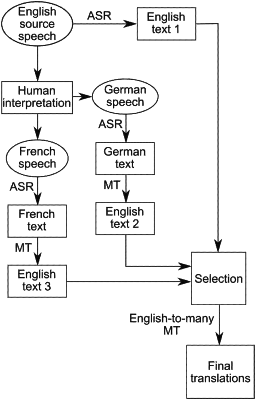
1. A computer-implemented method of real time speech translation comprising the following steps:
Receiving, in real time, input data comprising a source speech in a source language;
Receiving, in real time, interpretation data comprising a real time human interpretation of the source speech into at least one interpretation language different from the source language;
Transcribing, in real time, at least part of the input data and at least part of the interpretation data into text data using at least one automatic speech recognition system;
Translating, in real time, the text data into one common language using at least one machine translation system;
Selecting repeatedly, based at least partially on the transcribed input data and the transcribed interpretation data translated into the common language, a currently most credible source of data, wherein the currently most credible source is selected from group comprising the machine translation systems and speech recognition systems providing text data in the common language;
Feeding data from the currently most credible source into at least one machine translation system for real time translation into at least one language different from the source language and different from the at least one interpretation language; and
Obtaining, in real time, at least one translation of the data outputted from the currently most credible source;
wherein in the step of selecting, sources that have not provided any text data in a predetermined time period are ruled out from the current selection, current automatic credibility score of each of the remaining sources is determined based on outputs provided by each source in last N seconds, and the source with the best automatic credibility score is selected as the currently most credible source.
|