| CPC A61B 5/14865 (2013.01) [A61B 5/1451 (2013.01); A61B 5/14532 (2013.01); A61L 31/04 (2013.01); A61L 31/14 (2013.01); C09D 5/1681 (2013.01); C12Q 1/006 (2013.01); C12Q 1/26 (2013.01); C12Q 1/54 (2013.01); A61B 5/41 (2013.01); A61L 2400/18 (2013.01)] | 4 Claims |
|
1. A method of avoiding an inflammatory response to an implanted medical device comprising implanting the implantable medical device having a surface adapted to contact an in vivo environment, the surface comprising a polyimide composition having the following characteristics:
a carbon-to-oxygen ratio greater than 5 to 1;
a surface hydrophobicity of between 75° and 90°;
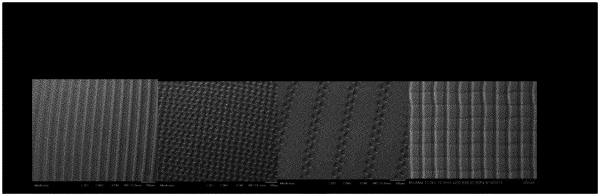
a surface topography characterized by at least one of (a)-(c):
(a) grooves having an average peak-to-valley height of between 0.3 μm and 5 μm;
(b) wells having an average peak-to-valley height of between 1 μm and 2 μm; and
(c) grids having an average peak-to-valley height of between 2 μm and 4 μm;
wherein:
the surface avoids the inflammatory response by having surface characteristics such that when exposed to the surface comprising the polymer composition, RAW264.7 macrophages are influenced to differentiate into an anti-inflammatory (M2) phenotype.
|