| CPC G06T 7/0012 (2013.01) [G06N 3/04 (2013.01); G16H 30/40 (2018.01); G06T 2207/10081 (2013.01); G06T 2207/10088 (2013.01); G06T 2207/20081 (2013.01); G06T 2207/20084 (2013.01); G06T 2207/30004 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
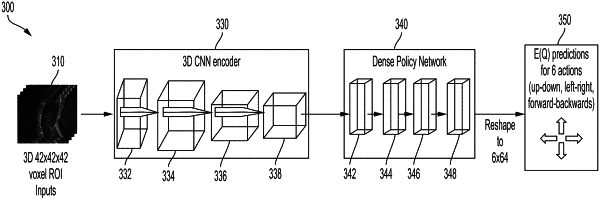
1. A method for anatomical landmark detection, the method comprising:
generating, using a first machine learning sub-network of an anatomical landmark detection agent, one or more image features for a cropped region of interest of a three-dimensional (3D) medical image, wherein the cropped ROI comprises a subset of the 3D medical image centered on a current location of the anatomical landmark detection agent within the 3D medical image;
providing to a second machine learning sub network the one or more image features for use in generating Q-values corresponding to allowable movement directions to be taken by the anatomical landmark detection agent;
generating, using at least a softmax layer of the second machine learning sub-network of the anatomical landmark detection agent for a set of six allowable movement directions associated with movement of the anatomical landmark detection agent within the 3D medical image, six corresponding discrete Q-value distributions wherein the set of six allowable movement directions comprise orthogonal image directions of the 3D medical image and wherein each discrete Q-value distribution:
comprises a predicted value distribution associated with moving the anatomical landmark detection agent from the current location within the 3D medical image, in the respective allowable movement direction;
predicting an anatomical landmark location within the 3D medical image using the plurality of discrete Q-value distributions based on moving the anatomical landmark detection agent within the 3D medical image, wherein in a given state the anatomical landmark detection agent moves in a selected allowable movement direction having a Q-value which is a maximum discrete Q-value distributions expected value over the set of six allowable movement directions; and
determining an uncertainty measure for the predicted anatomical landmark location, wherein the uncertainty measure is determined based on an average full width half maximum (FWHM) value calculated using the respective discrete Q-value distribution having the maximum expected value over the set of six allowable movement directions for the given state.
|