| CPC H04L 9/3271 (2013.01) [H04L 9/0825 (2013.01); H04L 9/088 (2013.01); H04L 9/321 (2013.01); H04L 9/3265 (2013.01)] | 11 Claims |
|
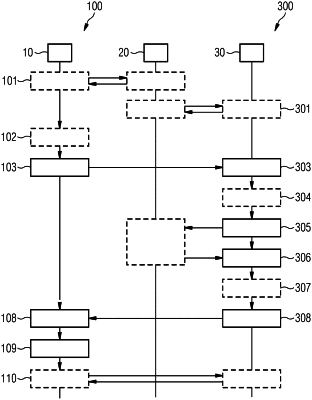
1. A method of operating a remote server device for establishing secure communication with an Internet of Things (IoT) client device, the method being performed by the remote server device, the method comprising:
receiving a query from the IoT client device for a proof of identity of the remote server device, the query being based on a challenge issued by the IoT client device, wherein the challenge has a predefined limited period of validity to prevent replay attacks;
prompting a trusted third party for the proof of identity of the remote server device;
receiving a response from the trusted third party comprising the proof of identity of the remote server device;
sending a response to the query, the response being based on the challenge and being indicative of the proof of identity of the remote server device; and
transmitting an absolute time reference from the remote server device to the IoT client device in response to a successful verification of an identity of the remote server device by the IoT client device, wherein the verification is done within the predefined limited period of validity,
wherein the query comprises the challenge being encrypted using a result of an operation based on a public key of the remote server device, the public key of the remote server device being signed by the trusted third party,
wherein the proof of identity of the remote server device comprises a signature issued by the trusted third party using a private key of the trusted third party, the signature comprising: (1) the challenge being decrypted using a secret key of the remote server device and (2) the public key of the remote server device, and
wherein the response comprises the proof of identity of the remote server device being encrypted using a result of an operation based on a public key of the IoT client device, the public key of the IoT client device being signed by the trusted third party.
|