| CPC H04L 63/105 (2013.01) [H04L 9/0656 (2013.01); H04L 63/1483 (2013.01); H04L 69/22 (2013.01); H04L 69/28 (2013.01)] | 18 Claims |
|
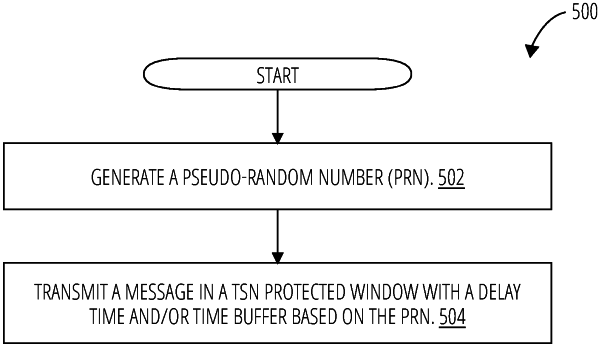
1. A computing-implemented method, comprising:
generating a pseudo-random number (PRN); and
transmitting a message during a protected transmission window of a data stream based on the PRN and a time buffer (TB), a plurality of switching nodes communicating via the data stream, wherein a one of the plurality of switching nodes can independently generate the PRN.
|