| CPC H02M 7/5395 (2013.01) [H02M 1/36 (2013.01); H02M 3/33584 (2013.01); H02M 7/487 (2013.01); H02M 7/797 (2013.01)] | 8 Claims |
|
1. A converter, comprising:
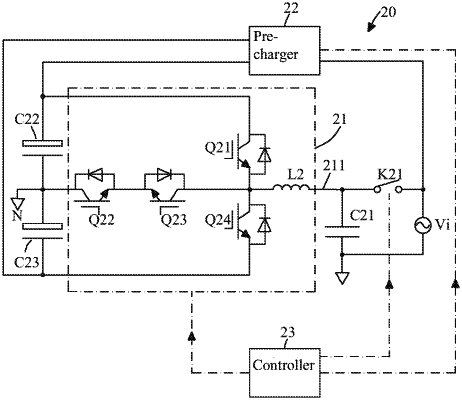
a bidirectional DC-AC converter circuit;
an input capacitor connected to an AC input of the bidirectional DC-AC converter circuit;
a bus capacitor connected to a DC output of the bidirectional DC-AC converter circuit;
a switch connected between a positive terminal of the input capacitor and an AC power supply;
a pre-charger circuit having an input connected to the AC power supply and an output connected to the DC output of the bidirectional DC-AC converter circuit; and
a controller configured to cause the pre-charger circuit to charge the bus capacitor while the switch is turned off and to cause the bidirectional DC-AC converter circuit to generate an inverting voltage from a voltage across the bus capacitor and apply the inverting voltage to the input capacitor before turning on the switch, wherein a phase of the inverting voltage is the same as a phase of a voltage of the AC power supply and wherein an amplitude of the inverting voltage is equal to an amplitude of the voltage of the AC power supply,
wherein the bus capacitor comprises a positive direct current bus capacitor and a negative direct current bus capacitor and a negative terminal of the positive direct current bus capacitor and a positive terminal of the negative direct current bus capacitor are connected to a neutral point;
wherein the bidirectional DC-AC converter circuit is a three-level converter and a DC output of the three-level converter is connected to a positive terminal of the positive direct current bus capacitor and a negative terminal of the negative direct current bus capacitor; and
wherein the controller is configured to control the pre-charger circuit such that an amplitude of a voltage across the positive direct current bus capacitor or negative direct current bus capacitor is equal to the amplitude of the AC power supply and to control the bidirectional DC-AC converter circuit such that the phase and amplitude of the inverting voltage are equal to the phase and amplitude of the AC power supply, respectively.
|