| CPC H02K 1/2766 (2013.01) [H02K 21/14 (2013.01); H02K 29/03 (2013.01); H02K 2213/03 (2013.01)] | 18 Claims |
|
1. A rotary electrical machine for motor vehicles, comprising:
a stator comprising a stator body provided with teeth delimiting notches, and a winding accommodated in the notches of the stator body;
a rotor comprising a rotor body and poles formed by permanent magnets,
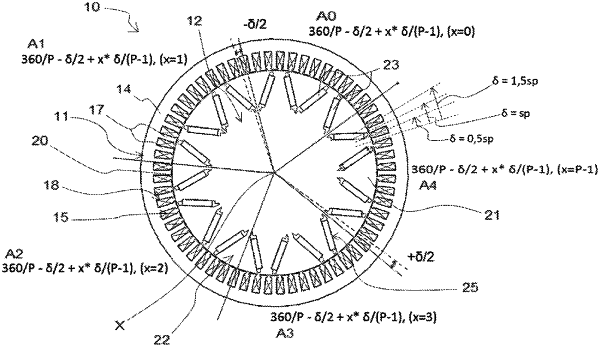
wherein two successive polar angles each corresponding to a circumferential extent of a pole, or two successive double polar angles each corresponding to a circumferential extent of two adjacent poles have an angular difference from one another which depends on an angular offsetting parameter associated with a stator pitch that is defined as being equal to 360 divided by a number of the teeth;
wherein a double polar angle of the two successive double polar angles is defined by the following equation:
Ax=360/P−δ/2+x*δ/(P−1)
x being the rank of the double polar angle, i.e. a whole number contained between 0 and P−1, P being the number of pairs of poles, and δ being the angular offsetting parameter.
|